What is Monetary Policy All About?
- 4m0•
- 08 May 2023
What is the price of the money?
Eh, does that even make sense? Yes. It does. This is what a monetary policy does. To regulate the price and supply of the money.
Let’s understand this with an analogy:
Farm and Irrigation: India and RBI
Imagine if India were a farm, and the RBI is the company in charge of irrigation. Its job is to keep water (money) flowing enough to maximize crops (strong employment, economic growth). But not pump in so much water as to cause flooding (inflation).
Monetary Policy operates in the similar way. It is a tool used by central banks (RBI) to regulate growth, inflation, unemployment and currency exchange rates.
Irrigation Agency: MPC
The RBI’s Monetary Policy Committee (MPC) has experience and knowledge about how the controls on its reservoir work and how much to open the valves to get ample amount of water onto the fields. Accordingly, the MPC resorts to expansionary or contractionary policy measures to increase or decrease the money supply in an economy.
Equipment: Quantitative & Qualitative Measures
RBI uses various quantitative and qualitative instruments like Repo rate, Reverse Repo rate, Statutory Liquidity Ratio, Cash Reserve Ratio, Open Market Operations, Moral Suasion etc. to achieve its purpose. However, on the day of the monetary policy (happens bi-monthly in India), all market participants’ eyes are mainly on the repo and reverse repo rate.
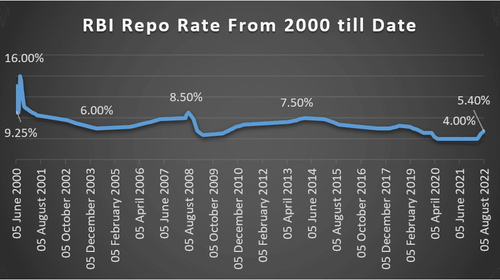
Repo rate is basically the rate at which the RBI lends money to commercial banks against the eligible government securities. When commercial banks run out of funds, they turn to RBI for help. So, when the repo rate is low, banks get funds from the RBI at a cheaper rate. Low rates encourage consumption. On the other hand, when repo rate is hiked, market interest rates will rise too. Thereby decrease in consumption and investments, and reduction in the demand. This will eventually lead to a decrease in the rate of inflation.
Meanwhile, the reverse repo rate is the rate at which the RBI absorbs liquidity from banks against the collateral of eligible government securities.
India and the Monetary Policy
Note that, repo rate also has an impact on the exchange rate. The hike in repo rate would encourage imports and discourage export; however, achieving all the goals through one policy alone is not possible. In every step, there is a trade-off. So, if inflation reduces, exports suffer and vice versa.
Besides, a combination of or other measures could also be implemented by the MPC to tackle the economic problems.
If we speak of current Indian scenario, MPC has raised repo rates last three times. Amid heightened risk of recession, the RBI maintained its inflation projection at 6.7% in FY23 and real GDP growth projection at 7.2%. The MPC decided to remain focused on withdrawal of accommodation to ensure inflation remains within the target going forward. The RBI aims to achieve the medium-term target for consumer price index (CPI) inflation of 4% within a band of +/- 2%, while supporting growth.
A look at Repo rate and Inflation rate in India over the years:
Source: freefincal.com/rbi-repo-rate-history, RBI’s Database on Indian Economy
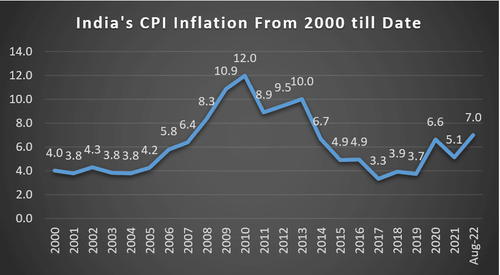
Source: Worldbank, tradingeconomics
Now that you know how monetary policy works, can you tell whether RBI will raise, reduce or maintain the repo rate in the upcoming meet?
References:
